How Do You Know if You Have a Cracked Skull After a Concussion
Head Injury
Not what you're looking for?
What is a caput injury?
A head injury is a broad term that describes many injuries that occur to the scalp, skull, brain, and underlying tissue and blood vessels in the caput. Head injuries are also normally referred to as encephalon injury, or traumatic brain injury (TBI), depending on the extent of the head trauma.
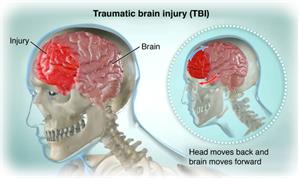
Caput injuries are one of the most mutual causes of disability and death in adults. The injury tin can exist equally mild equally a crash-land, bruise (contusion), or cut on the head. Or it can be moderate to astringent in nature due to a concussion, deep cutting or open up wound, fractured skull bone(s), or from internal bleeding and harm to the encephalon.
These are some of the different types of head injuries:
- Concussion. A concussion is an injury to the head area that may crusade instant loss of sensation or alertness for a few minutes up to a few hours later on the traumatic result.
- Skull fracture. A skull fracture is a pause in the skull bone. There are four major types of skull fractures:
- Linear skull fractures. This is the most common type of skull fracture. In a linear fracture, at that place is a interruption in the bone. Only it does not motility the bone. For this type of fracture, your healthcare provider may observe you lot in the hospital for a brief time. Normally, you volition non demand treatment and you lot can resume normal activities in a few days.
- Depressed skull fractures. You may or may not have a cutting in the scalp with this type of fracture. In this fracture, part of the skull is actually sunken in from the trauma. This type of skull fracture may require surgery, depending on the severity, to help correct the deformity.
- Diastatic skull fractures. These fractures occur along the suture lines in the skull. The sutures are the areas between the bones in the caput that fuse during childhood. In this blazon of fracture, the normal suture lines are widened. Newborns and older infants are more probable to get these types of fractures.
- Basilar skull fracture. This is the almost serious type of skull fracture. It involves a break in the os at the base of operations of the skull. With this type of fracture, you lot may have bruises effectually the eyes and a bruise behind the ear. Y'all may also have clear fluid draining from the nose or ears due to a tear in part of the covering of the brain. If you take this type of fracture, you will require close observation in the hospital.
- Intracranial hematoma (ICH). An intracranial hematoma is a claret clot in or around the encephalon. There are different types of hematomas. They are classified by their location in the brain. These tin can cause mild head injuries to quite serious and potentially life-threatening injuries. The different types of intracranial hematomas include:
- Epidural hematoma. Epidural hematomas occur when a blood jell forms underneath the skull, but on acme of the tough covering that surrounds the brain (the dura). They normally come from a tear in an avenue that runs just nether the skull. Epidural hematomas are usually associated with a skull fracture.
- Subdural hematoma. Subdural hematomas occur when a blood jell forms underneath the skull and underneath the dura, but exterior of the brain. These can grade from a tear in the veins that get from the brain to the dura, or from a cutting on the brain itself. They are sometimes, but non always, associated with a skull fracture.
- Contusion or intracerebral hematoma. A contusion is a bruise to the encephalon itself. A contusion causes bleeding and swelling inside of the encephalon around the surface area where the head was struck. Contusions may occur forth with a fracture or other blood clots.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage. This is when there is bleeding into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), the fluid that covers the encephalon. It is often linked with a subdural hemorrhage or contusion.
- Diffuse axonal injury (DAI). These injuries are common and are usually caused by shaking of the encephalon back and forth, which can happen in car accidents, from falls, or shaken baby syndrome. Diffuse injuries can be balmy, such as with a concussion, or may exist very severe, as in diffuse axonal injury. If severe, you may be in a coma for a prolonged period, with injury to many different parts of the brain.
- Penetrating injuries. These can result from bullets or other projectiles.
What causes a caput injury?
There are many causes of caput injury in children and adults. The nearly mutual traumatic injuries are from motor vehicle accidents (automobiles, motorcycles, or struck equally a pedestrian), violence, falls, or child abuse. Subdural hematomas and brain hemorrhages tin can sometimes happen spontaneously. The most mutual causes of head injury depend on age. Older adults tend to be at risk from falls, while younger people may be more at risk from contact sports, motor vehicle accidents, or violence.
When there is a straight blow to the head, shaking of the child, or when a whiplash-type injury occurs, the brain jolts backwards and hits the skull on the opposite side, causing a bruise. The jarring of the brain confronting the sides of the skull can crusade violent of the internal lining, tissues, and blood vessels that may cause internal bleeding, bruising, or swelling of the brain.
Who is at risk for a head injury?
Young children, older adults, and males are nigh at risk for head injuries. Those who don't use child car seats, seat belts, or rubber helmets are besides at increased risk for head injuries. People nether the influence of alcohol or drugs are more likely to have a head injury.
What are the symptoms of a head injury?
Symptoms vary depending on the severity of the head injury. These are the most common symptoms of a caput injury.
Mild head injury
Symptoms include:
- Raised, swollen area from a bump or a bruise
- Small, superficial (shallow) cut in the scalp
- Headache
- Sensitivity to noise and low-cal
- Irritability
- Confusion
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Problems with balance
- Nausea
- Bug with memory or concentration
- Change in sleep patterns
- Blurred vision
- "Tired" optics
- Ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Alteration in gustatory modality
- Fatigue or sluggishness
Moderate to astringent head injury
This requires medical attention correct away. Symptoms may include any of the above plus:
- Loss of consciousness
- Severe headache that does not go away
- Repeated nausea and vomiting
- Loss of short-term retentiveness, such as difficulty remembering the events that led right up to and through the traumatic result
- Slurred oral communication
- Trouble walking
- Weakness in one side or area of the trunk
- Sweating
- Pale skin colour
- Seizures or convulsions
- Behavior changes, including irritability
- Blood or clear fluid draining from the ears or nose
- Ane pupil (nighttime surface area in the eye of the eye) is dilated, or looks larger, than the other center and doesn't tuck, or get smaller, when exposed to calorie-free
- Deep cut or laceration in the scalp
- Open wound in the caput
- Strange object penetrating the head
- Coma (when you are unconscious and tin can't be awakened, don't respond to stimuli)
- Vegetative land (when you have lost thinking abilities and awareness of your surround simply can do basic functions such as breathing and blood circulation)
- Locked-in syndrome (a neurological condition in which a person is conscious and can recall and reason merely can't speak or move)
The symptoms of a head injury may look like other problems or medical atmospheric condition. Ever see your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
How is a head injury diagnosed?
The full extent of the head injury may non be completely understood immediately later the injury. You will need comprehensive evaluation and testing. A concrete test and other tests aid brand the diagnosis of a caput injury. During the test, the healthcare provider will ask about your medical history and how you were injured. Trauma to the head can crusade neurological problems and may require further medical follow upward.
Diagnostic tests may include:
- Blood tests.
- X-ray. This exam uses electromagnetic energy beams to make images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film.
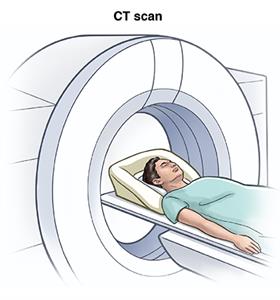
- CT scan. This procedure uses a combination of 10-rays and a calculator to brand detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fatty, and organs. CT scans are more detailed than general X-rays.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG). This procedure records the encephalon'south continuous, electric activity past means of electrodes fastened to the scalp.
- MRI. This exam uses large magnets, radio waves, and a estimator to make detailed images of organs and structures in the trunk. It does not apply X-rays.
How is a head injury treated?
Handling will depend on your symptoms, age, and general health. It will likewise depend on how severe the status is.
Depending on the severity of the injury, handling may range from ice and rest to observation to surgery.
For a astringent head injury, yous are monitored for increased intracranial force per unit area (pressure inside the skull). Head injury may cause the brain to swell. Since the brain is covered by the skull, there is merely a small corporeality of room for it to swell. This causes pressure level inside the skull to increase, which tin pb to encephalon damage.
Intracranial pressure is measured in 1 of two ways.
- 1 mode is to place a small hollow tube (catheter) into the fluid-filled space in the brain (ventricle).
- The second way is to utilize a small, hollow device (bolt) placed through the skull into the space just between the skull and the encephalon.
Your healthcare provider will insert i or both devices in the intensive care unit (ICU) or in the operating room. They will then adhere the device to a monitor that gives a abiding reading of the pressure inside the skull. If the pressure goes upwardly, it can exist treated right away. While the device is in identify, you will exist given medicine to stay comfortable. Your healthcare provider volition remove the device when the swelling has gone down and there is little chance of more swelling.
What are possible complications of a head injury?
A caput injury tin effect in loss of muscle forcefulness, fine motor skills, speech communication, vision, hearing, or taste function, depending on the brain region involved and the severity of brain harm. Long- or short-term changes in personality or behavior may also occur. You may need long-term medical and rehabilitative (physical, occupational, or speech communication therapy) management.
What can I do to forestall a head injury?
The primal to head injury prevention is to promote a condom surroundings for children and adults and to prevent head injuries from occurring in the first place. The post-obit measures can help prevent head injury:
- Use car seats and seat belts when riding in the car and helmets (when worn correctly) for activities such every bit bicycle riding, in-line skating, skiing, skateboarding, and other sports.
- Prevent falls. Since older adults are prone to falls, it is important to brand their living areas rubber past removing throw rugs or clutter that may cause them to trip. Install handrails in the bath and stairways, and be sure that there is expert lighting.
- For immature children, it is important to secure windows with window guards and safety gates.
When should I call my healthcare provider?
Seek medical attention right abroad if any of these occur:
- A cutting (laceration)
- Persistent or increasing sleepiness or confusion
- Seizure, repeated vomiting, or severe headache
- Inability to feel an arm or leg or recognize people
- Loss of balance
- Difficulty speaking, seeing, or animate
- Loss of consciousness
Cardinal points about caput injury
- A head injury is a broad term that describes many injuries that occur to the scalp, skull, brain, and underlying tissue and claret vessels in the caput.
- The virtually mutual traumatic injuries are from motor vehicle accidents, violence, falls, or child abuse.
- Moderate to severe caput injury requires firsthand medical attention.
- Severe head injury requires shut monitoring for increased intracranial force per unit area.
- Prevention is most important. Promote a safe surround for children and adults through the use of car seats, seat belts, and helmets. Likewise remove tripping and fall hazards in the home.
Next steps
Tips to assistance you get the most from a visit to your healthcare provider:
- Know the reason for your visit and what you want to happen.
- Before your visit, write down questions you want answered.
- Bring someone with y'all to assist you ask questions and remember what your provider tells you.
- At the visit, write downwards the name of a new diagnosis and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. Likewise write downward any new instructions your provider gives you.
- Know why a new medicine or handling is prescribed and how it will help yous. Also know what the side effects are.
- Enquire if your status tin be treated in other ways.
- Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean.
- Know what to expect if you exercise non take the medicine or have the exam or procedure.
- If yous accept a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose for that visit.
- Know how you can contact your provider if yous have questions.
Medical Reviewer: Joseph Campellone Md
Medical Reviewer: Rita Sather RN
Medical Reviewer: Raymond Kent Turley BSN MSN RN
© 2000-2021 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is non intended as a substitute for professional person medical intendance. Always follow your healthcare professional'south instructions.
Not what you lot're looking for?
Source: https://www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/diseases-and-conditions/h/head-injury.html
0 Response to "How Do You Know if You Have a Cracked Skull After a Concussion"
Post a Comment